23. OpenStack周期性任务分析¶
OpenStack 定时任务实现由两种实现方法,一种是通过 periodic_task 函数装饰器,
另外一种是由 DynamicLoopingCall 和 FixedIntervalLoopingCall
类通过协程来实现。
这两种定时任务的目的也完全不一样,前者一般都是用来装饰 nova-rpc-server 的 manager 类方法,用来实现资源定时刷新、状态报告等;后者通过 wait() 调用进行阻 塞,等待某些某些特定事件发生!
23.1. 阻塞型定时任务¶
对于第二种用法,源码比较简单,主要用到的是 eventlet.event.Event 类!让我们
首先来看看该类的用法。
from eventlet import event
import eventlet
import time
evt = event.Event()
def baz(b):
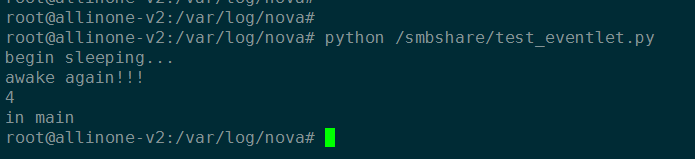
print "begin sleeping..."
time.sleep(10)
evt.send(b + 1)
print "awake again!!!"
_ = eventlet.spawn_n(baz, 3)
print evt.wait()
print "in main"
程序运行结果:
根据官网文档,event和queue差不多,但是有两个不同:
- 调用 send() 不会交出自己的cpu时间
- send() 只能被调用一次
event主要用于在不同协程间传递返回值。比如我协程A需要等协程B做了某件事后的结 果,那么我协程A可以建立了一个event evt,然后调用evt.wait()就会开始等待。协程 B把事情做好后运行evt.send(XXX) [注意,由于都在一个线程中,所以获取这个 evt 甚至不需要锁],这个时候协程A的evt.wait()代码就可以往下运行了,并且Hub会把相关的结果给它。
简言之,Event.wait() 是一个阻塞调用,等待 Event.send() 调用解除阻塞。
Note
以上例子,通过 spawn_n() 函数启动一个新协程,但是假如不执行最后 的 evt.wait(),那么 baz() 函数不会执行,结果没有任何输出。个人猜想 是,协程是主动让出cpu,假如不执行 evt.wait() 当前程序不会让出cpu, 那么新开启的协程也就没有机会调度运行。然后程序结束,直接退出,因此 不会有任何输出。当然,这只是个人猜想,得抽时间,好好熟悉下协程的 原理!
有了上面的简单例子作为基础后,我们利用 OpenStack 的 FixedIntervalLoopingCall
创建一个定时任务。来看例子:
#!/usr/bin/env python2
#from nova import utils
from nova.openstack.common.loopingcall import FixedIntervalLoopingCall
from nova.openstack.common.loopingcall import LoopingCallDone
#import inspect
import eventlet
count = 0
def panda(tagline):
global count
count += 1
print "#", count, "Panda.", tagline
if count >= 3:
#raise utils.LoopingCallDone
print "Looping call Done, bye..."
raise LoopingCallDone
periodic = FixedIntervalLoopingCall(panda, "hello world!")
#periodic.start(interval=0.8753)
periodic.start(1, 2)
periodic.wait()
来看看程序运行结果:
root@allinone-v2:/smbshare# python periodic_fun.py
# 1 Panda. hello world!
2016-12-24 23:23:33.346 10839 WARNING nova.openstack.common.loopingcall [-] task <function panda at 0x7f5c5e2ac578> run outlasted interval by 1.00 sec
# 2 Panda. hello world!
2016-12-24 23:23:35.351 10839 WARNING nova.openstack.common.loopingcall [-] task <function panda at 0x7f5c5e2ac578> run outlasted interval by 1.00 sec
# 3 Panda. hello world!
Looping call Done, bye...
在程序中,我们设置定时任务执行三次。现在根据这个例子,来
分析下 FixedIntervalLoopingCall 的源码:
class LoopingCallBase(object):
def __init__(self, f=None, *args, **kw):
self.args = args
self.kw = kw
self.f = f
self._running = False
self.done = None
def stop(self):
self._running = False
def wait(self):
return self.done.wait()
class FixedIntervalLoopingCall(LoopingCallBase):
"""A fixed interval looping call."""
def start(self, interval, initial_delay=None):
self._running = True
done = event.Event()
def _inner():
if initial_delay:
greenthread.sleep(initial_delay)
try:
while self._running:
start = _ts()
self.f(*self.args, **self.kw)
end = _ts()
if not self._running:
break
delay = end - start - interval
if delay > 0:
LOG.warn(_LW('task %(func_name)s run outlasted '
'interval by %(delay).2f sec'),
{'func_name': repr(self.f), 'delay': delay})
greenthread.sleep(-delay if delay < 0 else 0)
except LoopingCallDone as e:
self.stop()
done.send(e.retvalue)
except Exception:
LOG.exception(_LE('in fixed duration looping call'))
done.send_exception(*sys.exc_info())
return
else:
done.send(True)
self.done = done
greenthread.spawn_n(_inner)
return self.done
- 首先,实例化
FixedIntervalLoopingCall对象,保存协程要执行的函数,函数参数等; - 然后执行
periodic.start(1, 2), 注意,执行该函数时,只是设置 interval, initial_delay 参数,并利用闭包函数新建一个协程。此时,inner 函数还并没有机会投入运行! - 主控程序 periodic.wait(), 让出CPU,接下来的 _inner 函数有机会执行,并统计函数执行时间, 依据时间差进入睡眠状态,等待下一次调度执行!
Tip
根据这个例子,我们可以知道,假如定时任务执行后,除非定时任务
执行完成,否则代码 periodic.wait() 会永远阻塞。可是 OpenStack 组件一般
有很多定时任务,那么他们是如何做到同时执行的呢。这个问题待结合OpenStack相关代码
进行分析,待完成。
初步猜想,可能是在线程中启动协程。这样就可以开启多个定时任务,待验证!
update: 2017-1-4 17:00
根据补充的通知型定时任务分析可知,并非用到了什么多线程,实际上,nova是在一个函数
PeriodicTasks.run_periodic_tasks() 中循环调用所有的定时任务来实现的。
update: 2017-1-3 17:00
另外,根据源码可知,_inner() 函数内部是一个循环,只有捕获 LoopingCallDone 异常才会
停止任务并通过 done.send() 解除 done.wait() 阻塞。因此,一般对于这类定时任务在要调用的函数
内部,抛出 LoopingCallDone 异常。nova源码中也有类似的处理:比如 libvirt 启动虚拟机时,
就一直阻塞等待虚拟机状态为 RUNNING 。
nova/virt/libvirt/driver.py
def spawn(self, context, instance, image_meta, injected_files,
admin_password, network_info=None, block_device_info=None):
def _wait_for_boot():
"""Called at an interval until the VM is running."""
state = self.get_info(instance)['state']
if state == power_state.RUNNING:
LOG.info(_LI("Instance spawned successfully."),
instance=instance)
raise loopingcall.LoopingCallDone()
timer = loopingcall.FixedIntervalLoopingCall(_wait_for_boot)
timer.start(interval=0.5).wait()
23.2. 状态报告和通知型定时任务¶
下面以 nova-scheduler 服务为例,分析第二种定时任务。
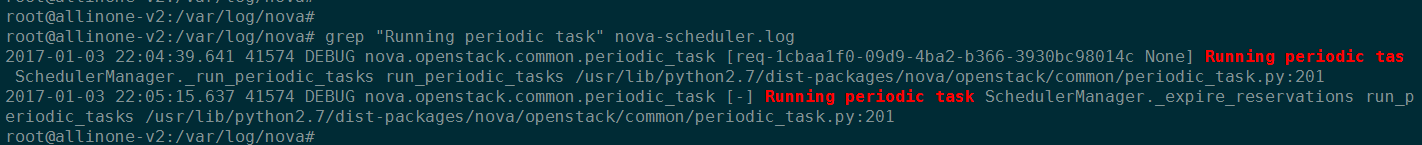
我们可以开启 --debug 选项,然后通过日志查看调用的定时任务:
nova-scheduler --debug
root@allinone-v2:/var/log/nova# grep "Running periodic task" nova-scheduler.log
2017-01-03 22:04:39.641 41574 DEBUG nova.openstack.common.periodic_task [req-1cbaa1f0-09d9-4ba2-b366-3930bc98014c None] Running periodic tas SchedulerManager._run_periodic_tasks run_periodic_tasks /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/openstack/common/periodic_task.py:201
2017-01-03 22:05:15.637 41574 DEBUG nova.openstack.common.periodic_task [-] Running periodic task SchedulerManager._expire_reservations run_periodic_tasks /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/openstack/common/periodic_task.py:201
2017-01-03 22:05:39.650 41574 DEBUG nova.openstack.common.periodic_task [-] Running periodic task SchedulerManager._run_periodic_tasks run_periodic_tasks /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/openstack/common/periodic_task.py:201
nova.scheduler.manager.SchedulerManager
@periodic_task.periodic_task
def _expire_reservations(self, context):
QUOTAS.expire(context)
@periodic_task.periodic_task(spacing=CONF.scheduler_driver_task_period,
run_immediately=True)
def _run_periodic_tasks(self, context):
self.driver.run_periodic_tasks(context)
SchedulerManager 类有两个定时任务,我们来看看定时任务装饰器函数 periodic_task()
def periodic_task(*args, **kwargs):
"""Decorator to indicate that a method is a periodic task.
This decorator can be used in two ways:
1. Without arguments '@periodic_task', this will be run on the default
interval of 60 seconds.
2. With arguments:
@periodic_task(spacing=N [, run_immediately=[True|False]])
this will be run on approximately every N seconds. If this number is
negative the periodic task will be disabled. If the run_immediately
argument is provided and has a value of 'True', the first run of the
task will be shortly after task scheduler starts. If
run_immediately is omitted or set to 'False', the first time the
task runs will be approximately N seconds after the task scheduler
starts.
"""
def decorator(f):
# Test for old style invocation
if 'ticks_between_runs' in kwargs:
raise InvalidPeriodicTaskArg(arg='ticks_between_runs')
# Control if run at all
f._periodic_task = True
f._periodic_external_ok = kwargs.pop('external_process_ok', False)
if f._periodic_external_ok and not CONF.run_external_periodic_tasks:
f._periodic_enabled = False
else:
f._periodic_enabled = kwargs.pop('enabled', True)
# Control frequency
f._periodic_spacing = kwargs.pop('spacing', 0)
f._periodic_immediate = kwargs.pop('run_immediately', False)
if f._periodic_immediate:
f._periodic_last_run = None
else:
f._periodic_last_run = time.time()
return f
# NOTE(sirp): The `if` is necessary to allow the decorator to be used with
# and without parenthesis.
#
# In the 'with-parenthesis' case (with kwargs present), this function needs
# to return a decorator function since the interpreter will invoke it like:
#
# periodic_task(*args, **kwargs)(f)
#
# In the 'without-parenthesis' case, the original function will be passed
# in as the first argument, like:
#
# periodic_task(f)
if kwargs:
return decorator
else:
return decorator(args[0])
代码注释很清楚,这个装饰器就是给要定时运行的函数加上一些额外的属性,用来控制 定时任务函数的执行和执行频率等。
periodic.periodic_task() 装饰器是用来装饰 Manager 类的。
Manager 类的继承体系如下:
nova.scheduler.manager.SchedulerManager –> nova.manager.Manager
–> ( nova.db.base.Base, nova.openstack.common.periodic_task.PeriodicTasks)
其中, nova.openstack.common.periodic_task.PeriodicTasks 具有元类
_PeriodicTasksMeta
class _PeriodicTasksMeta(type):
def __init__(cls, names, bases, dict_):
"""Metaclass that allows us to collect decorated periodic tasks."""
super(_PeriodicTasksMeta, cls).__init__(names, bases, dict_)
# NOTE(sirp): if the attribute is not present then we must be the base
# class, so, go ahead an initialize it. If the attribute is present,
# then we're a subclass so make a copy of it so we don't step on our
# parent's toes.
try:
cls._periodic_tasks = cls._periodic_tasks[:]
except AttributeError:
cls._periodic_tasks = []
try:
cls._periodic_spacing = cls._periodic_spacing.copy()
except AttributeError:
cls._periodic_spacing = {}
for value in cls.__dict__.values():
if getattr(value, '_periodic_task', False):
task = value
name = task.__name__
if task._periodic_spacing < 0:
LOG.info(_LI('Skipping periodic task %(task)s because '
'its interval is negative'),
{'task': name})
continue
if not task._periodic_enabled:
LOG.info(_LI('Skipping periodic task %(task)s because '
'it is disabled'),
{'task': name})
continue
# A periodic spacing of zero indicates that this task should
# be run on the default interval to avoid running too
# frequently.
if task._periodic_spacing == 0:
task._periodic_spacing = DEFAULT_INTERVAL
cls._periodic_tasks.append((name, task))
cls._periodic_spacing[name] = task._periodic_spacing
需要注意这行代码: if getattr(value, '_periodic_task', False): ,
只有被 _periodic_task 修饰的函数,该行代码才返回真。
元类通过拦截 SchedulerManager 类的创建,使得类属性
cls._periodic_task 和 cls._periodic_spacing 保存有通过 _periodic_task 装饰器
装饰的定时任务函数信息。
然后我们来看看服务启动 Service.Start 函数:
nova/Service:Service.start
if self.periodic_enable:
if self.periodic_fuzzy_delay:
initial_delay = random.randint(0, self.periodic_fuzzy_delay)
else:
initial_delay = None
self.tg.add_dynamic_timer(self.periodic_tasks,
initial_delay=initial_delay,
periodic_interval_max=
self.periodic_interval_max)
nova/openstack/common/threadgroup:ThreadGroup.add_dynamic_timer
def add_dynamic_timer(self, callback, initial_delay=None,
periodic_interval_max=None, *args, **kwargs):
timer = loopingcall.DynamicLoopingCall(callback, *args, **kwargs)
timer.start(initial_delay=initial_delay,
periodic_interval_max=periodic_interval_max)
self.timers.append(timer)
add_dynamic_timer 函数不过是创建一个 DynamicLoopingCall 对象, 动态定时调用自身的 periodic_tasks 函数, 而该函数又调用相应的 Manager.periodic_task 函数:
nova/service:Service.periodic_task
def periodic_tasks(self, raise_on_error=False):
"""Tasks to be run at a periodic interval."""
ctxt = context.get_admin_context()
return self.manager.periodic_tasks(ctxt, raise_on_error=raise_on_error)
nova/manager:Manager.periodic_tasks
def periodic_tasks(self, context, raise_on_error=False):
"""Tasks to be run at a periodic interval."""
return self.run_periodic_tasks(context, raise_on_error=raise_on_error)
run_periodic_tasks 函数在具有元类 _PeriodicTasksMeta 的类 PeriodicTasks 中定义:
class PeriodicTasks(object):
def __init__(self):
super(PeriodicTasks, self).__init__()
self._periodic_last_run = {}
for name, task in self._periodic_tasks:
self._periodic_last_run[name] = task._periodic_last_run
def run_periodic_tasks(self, context, raise_on_error=False):
"""Tasks to be run at a periodic interval."""
idle_for = DEFAULT_INTERVAL
for task_name, task in self._periodic_tasks:
full_task_name = '.'.join([self.__class__.__name__, task_name])
spacing = self._periodic_spacing[task_name]
last_run = self._periodic_last_run[task_name]
# Check if due, if not skip
idle_for = min(idle_for, spacing)
if last_run is not None:
delta = last_run + spacing - time.time()
if delta > 0:
idle_for = min(idle_for, delta)
continue
LOG.debug("Running periodic task %(full_task_name)s",
{"full_task_name": full_task_name})
self._periodic_last_run[task_name] = _nearest_boundary(
last_run, spacing)
try:
task(self, context)
except Exception as e:
if raise_on_error:
raise
LOG.exception(_LE("Error during %(full_task_name)s: %(e)s"),
{"full_task_name": full_task_name, "e": e})
time.sleep(0)
return idle_for
从而最终实际上要调用的动态定时函数是 run_periodic_tasks ,在该函数中,会 依次调用所有的被 periodic_task 装饰器包装的函数。
最后,在 nova/cmd/scheduler.py 中执行 server.wait() 函数,经过一系列的
跳转调用后,最终调用 nova/openstack/common/threadgroup:ThreadGroup.wait 函数。
在该函数里面,会调用 Event.wait(),从而每个定时任务可以调度运行。
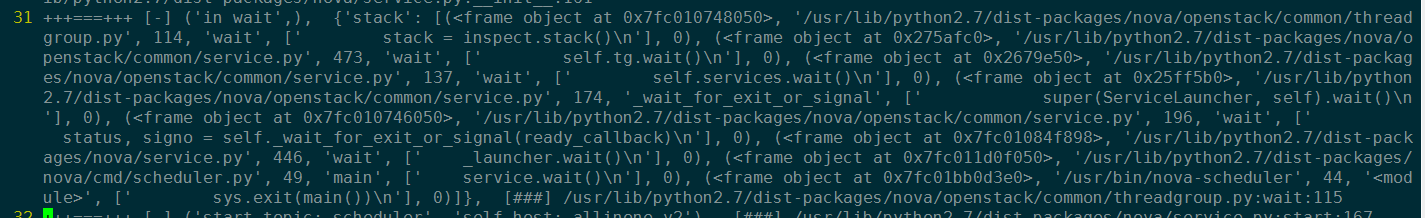
在wait函数中打印堆栈信息,查看调用跳转流程。
def wait(self):
import inspect;
stack=inspect.stack()
LOG_DEBUG("in wait", stack=stack)
for x in self.timers:
try:
x.wait()
except eventlet.greenlet.GreenletExit:
pass
except Exception as ex:
LOG.exception(ex)
current = threading.current_thread()
# Iterate over a copy of self.threads so thread_done doesn't
# modify the list while we're iterating
for x in self.threads[:]:
if x is current:
continue
try:
x.wait()
except eventlet.greenlet.GreenletExit:
pass
except Exception as ex:
LOG.exception(ex)
+++===+++ [-] ('in wait',),
{'stack':
[
(<frame object at 0x7fc010748050>, '/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/openstack/common/thread group.py', 114, 'wait', [' stack = inspect.stack()\n'], 0),
(<frame object at 0x275afc0>, '/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/o penstack/common/service.py', 473, 'wait', [' self.tg.wait()\n'], 0),
(<frame object at 0x2679e50>, '/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packag es/nova/openstack/common/service.py', 137, 'wait', [' self.services.wait()\n'], 0),
(<frame object at 0x25ff5b0>, '/usr/lib/python 2.7/dist-packages/nova/openstack/common/service.py', 174, '_wait_for_exit_or_signal', [' super(ServiceLauncher, self).wait()\n '], 0),
(<frame object at 0x7fc010746050>, '/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/openstack/common/service.py', 196, 'wait', [' status, signo = self._wait_for_exit_or_signal(ready_callback)\n'], 0),
(<frame object at 0x7fc01084f898>, '/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-pack ages/nova/service.py', 446, 'wait', [' _launcher.wait()\n'], 0), (<frame object at 0x7fc011d0f050>, '/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/ nova/cmd/scheduler.py', 49, 'main', [' service.wait()\n'], 0),
(<frame object at 0x7fc01bb0d3e0>, '/usr/bin/nova-scheduler', 44, '<module>', [' sys.exit(main())\n'], 0)]
},
[###] /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/openstack/common/threadgroup.py:wait:115
| [1] | http://www.cnblogs.com/yuhan-TB/p/4085074.html |