4. Linux命令和shell¶
目录
4.1. bash快捷键¶
ctrl + a; 定位光标到命令行首
ctrl + e; 命令行尾
ctrl + l; 清屏
!!:1 上一条命令第一个参数
!$ 上一条命令最后一个参数
ctrl + $; 搜索历史命令
4.2. bash编程¶
4.2.1. 正则匹配¶
cd /usr/bin
# 判断变量是否不包含bak字符
for i in nova-*; do [[ ! $i =~ "bak" ]] && echo $i ;done
4.2.3. 重定向和管道¶
我们来建立一个 test_redirect.sh 脚本来测试shell输入输出重定向和管道。
shell 脚本中流重定向方式 >&2 参考于 service 命令源码。
test_redirect.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo "stdout info"
echo "stdout info-2"
echo "stderr info" >&2
echo "stderr info-2" >&2
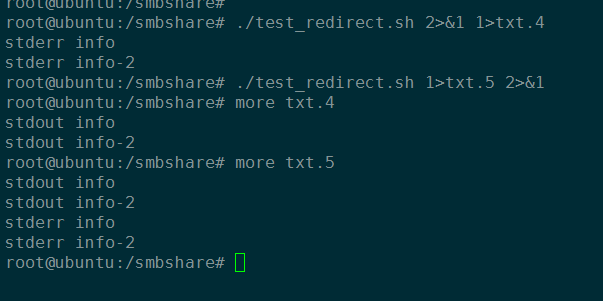
重定向测试一:
## 过滤 stderr 或者过滤 stdout
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ./test_redirect.sh 1>/dev/null
stderr info
stderr info-2
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ./test_redirect.sh 2>/dev/null
stdout info
stdout info-2
## stdout 和 stderr 重定向
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ./test_redirect.sh 1> txt.1
stderr info
stderr info-2
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ./test_redirect.sh 2> txt.2
stdout info
stdout info-2
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# more txt.1
stdout info
stdout info-2
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# more txt.2
stderr info
stderr info-2
## stdout 和 stderr 重定向到一个文件
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ./test_redirect.sh &> txt.3
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# more txt.3
stdout info
stdout info-2
stderr info
stderr info-2
重定向测试二:
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ./test_redirect.sh 2>&1 1>txt.4
stderr info
stderr info-2
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ./test_redirect.sh 1>txt.5 2>&1
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# more txt.5
stdout info
stdout info-2
stderr info
stderr info-2
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# more txt.4
stdout info
stdout info-2
可以看到,重定向顺序不同,结果差别很明显。因为 shell 从左到右的顺序处理重定向。
因此命令 ./test_redirect.sh 1>txt.5 2>&1 将标准输出和标准错误都重定向到文件 txt.5(
先将标准输出重定向到文件 txt.5 ,然后标准错误重定向到标准输出既 txt.5);
而命令 ./test_redirect.sh 2>&1 1>txt.4 先将标准错误重定向到标准输出(此时是终端),
然后将标准输出重定向到文件 txt.4 ;而标准错误目的地依然是终端。
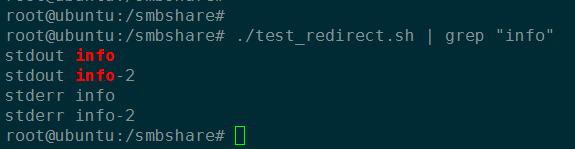
管道测试一:
根据grep高亮显示可以知道,默认情况下只有 stdout (标准输出流)重定向到管道; 标准错误流没有重定向到管道。
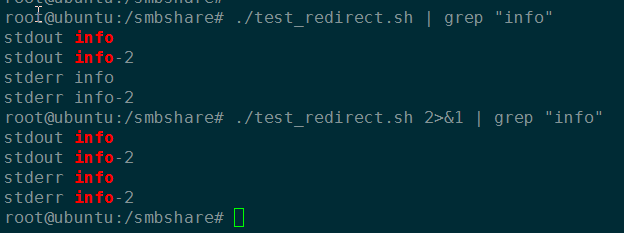
管道测试二:
根据搜索结果,可以看到,shell 先处理重定向,然后处理管道。因此,grep可以搜索到 stderr info信息(标准错误重定向到标准输入而来)。
4.2.4. 尖括号用法收集¶
bash编程中自己遇到的尖括号用法汇总。
流重定向¶
流重定向的尖括号的用法包括:
<,输入重定向;>,输出重定向;>>,追加重定向;
更多细节可以参考上一节。
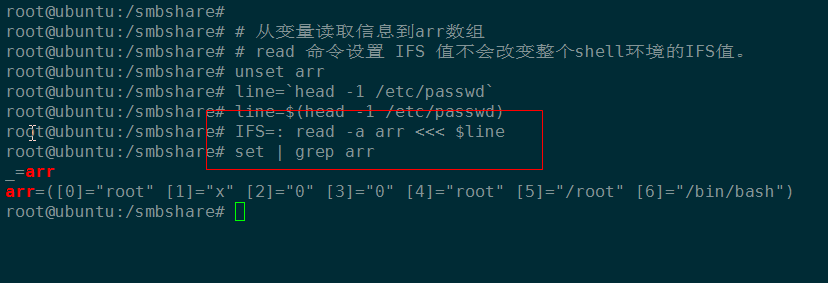
# 逐行读取并处理文件
while read line
do
echo $line
done < /etc/passwd
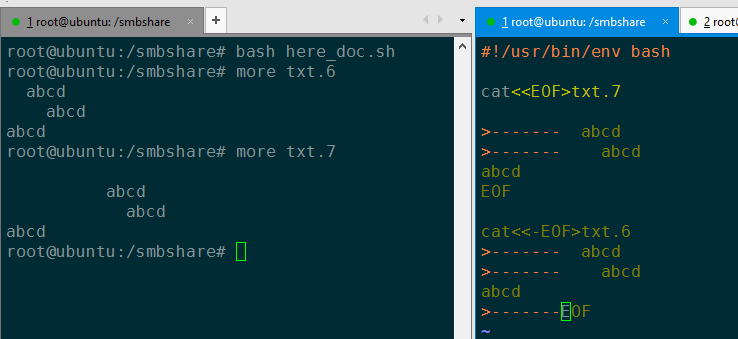
here-docement¶
有两种具体用法:
# here-document
cat<< EOF > /smbshare/5.txt
Here document
test,
bye!
EOF
# here-document,结果会删除每行行首的tab,空格不会删除!
cat<<- EOF > /smbshare/6.txt
Here document
test,
bye!
EOF
可以看到,<<- 形式的 here-docement,结果会删除行首的 tab;而 << 形式的则不会。
4.2.5. 字符串截取¶
url='http://10.10.10.10:35357/v2.0'
# 从最左边开始删除
echo ${SERVICE_ENDPOINT#*//}
#
echo ${SERVICE_ENDPOINT##*/}
| [1] | http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2015-03/115198.htm |
4.4. 常用命令¶
常用命令常用用法参考!
4.4.1. nc¶
传输目录
server端:
tar -cvf - allinone-v2.5-install-script | nc -l 12345
client端:
nc -n 192.168.159.146 12345 | tar -xvf -
传输文件
server端:
nc -l 12345 < file.txt
client端:
nc -n 172.31.100.7 12345 > file.txt
然后两端分别使用md5sum命令核对文件传输是否出错.
扫描端口
nc -v -w 1 10.11.111.50 -z 1-1000
4.4.2. apt-get¶
只获取包,不安装:
# 如果软件包没有安装
apt-get -d install git
# 如果已经安装
apt-get -d install git --reinstall
更新安装包索引:
apt-get update
升级已经安装的所有软件包:
apt-get upgrade
搜索包:
apt-cache search lvm
apt-cache search cifs | grep -i cifs
获取包的相关信息:
apt-cache show lvm2
安装特定版本:
apt-get --reinstall install neutron-common=1:2014.1.3-0ubuntu1.1
| [2] | http://os.51cto.com/art/200802/65583.htm |
| [3] | http://wiki.ubuntu.org.cn/Apt%E5%92%8Cdpkg%E5%BF%AB%E9%80%9F%E5%8F%82%E8%80%83 |
4.4.3. awk¶
awk -v FS=':' '{print $1}' /etc/passwd
# 打印某一行, 自设定分隔符
awk -F: '{print $1}' /etc/passwd
# 打印除第一行之外的所有行
awk '{$1="";print $0}' file
# 循环把前N列都赋值为空,从第n+1列开始打印所有的列!
awk '{ for(i=1; i<=n; i++){ $i="" }; print $0 }' urfile
# 以tab分隔符切割记录,输出也以tab作为分隔符。选择第二个字段为GET的记录!
awk -F'\t' -vOFS='\t' '{if ($2=="GET") print $1, $3}' ceph_meter.txt > ceph_meter_get.txt
# 打印每一行记录长度
awk '{print length}' df.txt
# 打印前两行记录长度
awk 'NR<=2{print length}' df.txt
| [4] | 对awk入门有很精彩的描述。http://www.zsythink.net/archives/1336 |
4.4.4. cut¶
echo "test/dev/mapper/juno" | cut -d '/' -f1
#test
echo "test/dev/mapper/juno" | cut -d '/' -f2
#dev
echo "test/dev/mapper/juno" | cut -d '/' -f2-
#dev/mapper/juno
echo "/dev/mapper/juno" | cut -d '/' -f1
#
echo "/dev/mapper/juno" | cut -d '/' -f2
#dev
| [5] | http://www.jb51.net/article/41872.htm |
4.4.5. dpkg¶
查看某软件包是否安装,这两条都可以:
dpkg -s lvm2
dpkg-query -l lvm
列出所有安装软件包:
dpkg --get-selections
dpkg -l
列出软件包中所有文件位置:
dpkg -L lvm2
手动安装deb包:
dpkg -i neutron-metering-agent_2014.2.1-0ubuntu1-cloud0_all.deb
查看deb包文件内容:
dpkg -c neutron-metering-agent_2014.2.1.deb
4.4.7. scp/rsync¶
# 远程拷贝文件
scp root@10.11.113.198:/smbshare/win7.raw .
# 远程拷贝目录
scp -r root@10.11.113.198:/smbshare/ .
rsync 命令是一个远程同步工具,也可以用来拷贝远程文件, 比如openstack虚机冷迁移都是通过该命令,来拷贝虚机磁盘文件的:
rsync -av /home/coremail/ 192.168.11.12:/home/coremail/
| [6] | http://coolnull.com/1899.html |
4.4.8. ssh¶
原来以为ssh是一个远程登录工具,实际上ssh还可以执行远程主机上的命令,结果输出到本地。
这种方式,也是从openstack nova项目源码学习到的。
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# nova -h
The program 'nova' is currently not installed. You can install it by typing:
apt-get install python-novaclient
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ssh root@192.168.159.155 nova -h
root@192.168.159.155's password:
usage: nova [--version] [--debug] [--os-cache] [--timings]
[--timeout <seconds>] [--os-auth-token OS_AUTH_TOKEN]
[--os-username <auth-user-name>] [--os-user-id <auth-user-id>]
[--os-password <auth-password>]
[--os-tenant-name <auth-tenant-name>]
[--os-tenant-id <auth-tenant-id>] [--os-auth-url <auth-url>]
[--os-region-name <region-name>] [--os-auth-system <auth-system>]
[--service-type <service-type>] [--service-name <service-name>]
[--volume-service-name <volume-service-name>]
[--endpoint-type <endpoint-type>]
[--os-compute-api-version <compute-api-ver>]
[--os-cacert <ca-certificate>] [--insecure]
[--bypass-url <bypass-url>]
<subcommand> ...
Command-line interface to the OpenStack Nova API.
.....
root@ubuntu:/smbshare# ssh 192.168.159.155 'nova -h | grep list'
root@192.168.159.155's password:
absolute-limits Print a list of absolute limits for a user
agent-list List all builds.
aggregate-list Print a list of all aggregates.
availability-zone-list List all the availability zones.
cloudpipe-list Print a list of all cloudpipe instances.
dns-domains Print a list of available dns domains.
dns-list List current DNS entries for domain and ip or
flavor-access-list Print access information about the given
flavor-list Print a list of available 'flavors' (sizes of
floating-ip-bulk-list List all floating ips.
floating-ip-list List floating ips.
floating-ip-pool-list List all floating ip pools.
host-list List all hosts by service.
hypervisor-list List hypervisors.
image-list Print a list of available images to boot from.
interface-list List interfaces attached to a server.
keypair-list Print a list of keypairs for a user
4.4.9. sed¶
修改文件某一行:
# 终端显示修改后的结果
sed "s/'metering',/'metering','instances_monitor'/g" txt
# 直接修改原文件
sed -i "26s/'metering',/'metering','instances_monitor'/g" dashboard.py
4.4.10. route¶
添加路由:
route add -net 224.0.0.0 netmask 240.0.0.0 dev eth0
删除路由:
route del -net 224.0.0.0 netmask 240.0.0.0
route del -net 224.0.0.0 netmask 240.0.0.0 reject
4.4.11. ps¶
# 批量杀死进程:
ps -aux|grep name|grep -v grep|cut -c 9-15|xargs kill -9
# 显示进程的父子关系
ps afx -o pid,cmd | grep nova
# 查看某bash的进程树
ps f
ps f | grep nova
4.4.12. df/du¶
df -hl
du -hd1
# 列出某个文件或目录占用的空间
du -sh dir
4.4.13. find¶
find . -type f -name "*.py" | xargs egrep "xxx"
| [7] | http://yansu.org/2014/01/15/general-shell-resources.html |
4.4.14. locate/updatedb¶
updatedb
# 以下两条命令等效
locate .git | grep -P ".git$"
locate -b .git
4.4.15. xargs¶
xargs和重定向的区别,网上有很多论述。可以通过一个例子来简单理解下:
root@ubuntu:/smbshare/MyBlogs# echo '--help' | xargs cat
Usage: cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Concatenate FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output.
-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line
-n, --number number all output lines
-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-t equivalent to -vT
-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I
-u (ignored)
-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Examples:
cat f - g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.
cat Copy standard input to standard output.
Report cat bugs to bug-coreutils@gnu.org
GNU coreutils home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'cat invocation'
root@ubuntu:/smbshare/MyBlogs# echo '--help' | cat
--help
输出结果一目了然,对于xargs,是将echo的输出”–help”当做cat命令的参数; 而重定向符合则是将输出当初cat命令的输入。差别还是很明显的。
来看其他几个例子,来理解下:
find . -type f -name "*.py" | xargs chmod 666
find . -type f -name "*.sh" | xargs chmod +x
xargs命令还有很多其他高级用法,可以参考man文档。
4.4.16. lsof¶
# 不带任何参数,则输出所有活跃进程的所有打开文件
lsof
# 获取网络连接信息
lsof -i
lsof -i tcp
# 查看某端口的文件信息
lsof -i :5000
# 查看文件别哪些进程打开
lsof /smbshare/csq.log
# 查看进程打开哪些文件
ps -ef | grep nova-sch
lsof -p pid
# 获取网络连接,查看所有的监听套接字和已连接套接字
lsof -i -P -n
# 其他
lsof -i@192.168.159.1 -P -n
lsof -i@192.168.159.1:22 -P -n
# 列出rabbitmq用户的所有网络连接!
# lsof 命令选项组合一般是或关系,所以需要使用 -a 选项变成 and关系!
ps -ef | grep rabbit
lsof -u rabbitmq -a -i -P -n
# 列出某进程的所有网络连接
lsof -p <pid> -a -i -P -n
这里需要解释下,服务端调用listen后,返回的是 监听套接字 ,然后客户端主动发起connect连接, 服务端accept后,返回 已连接套接字 。两者都可以通过lsof命令列出来!
lsof 还有很多其他的高级用法,可以参考:
| [8] | https://linux.cn/article-4099-1.html |
4.4.20. ln/unlink¶
# 建立硬链接
ln srcfile dstfile
# 建立软连接
ln -s srcfile dstfile
ln -s /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages pydist
# 显示软硬连接文件详情和区别、inode节点数!
ll tf-* -i
# 663182 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Dec 1 06:59 tf-hl
# 663237 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 13 Dec 1 07:01 tf-sl -> tmp/test-file
ll -i tmp/test-file
# 663182 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Dec 1 06:59 tmp/test-file
ln命令需要特别注意如下几点:
- 建立硬链接时拷贝inode节点。硬链接文件是普通文件(文件类型位为
-),永远不要建立目录的硬链接。 - 软连接可以连接文件、目录,inode节点数没有增加,文件类型位为
l。
删除链接文件时要特别注意,可能一不小心,就把链接文件指向的目录下所有内容就删除了。安全起见, 还是使用unlink命令删除一个链接!
4.4.21. grep¶
grep命令有很多选项,支持的正则表达式流派也很多。个人对prce流派正则比较熟悉,
日常中使用也主要是使用 -P 选项使用prce模式进行匹配!
# -P: 使用 pcre 模式搜索
# -v: 表示搜索不匹配的
# -i: 忽略大小写
git status | grep -Pv '\.pyc$'
# 使用-b零宽断言搜索整个单词
grep -P '\bMeteringPlugin\b' . -rn
# 搜索固定字符串, 否则 + 会被当成元字符
fgrep '+++===+++' /var/log/apache2/error.log
# 递归搜索
# -r: 递归搜索,不跟从符号链接!
fgrep -rn '+++===+++' .
4.4.24. tar¶
tar命令笔记常用:
tar -czf file.tar.gz a b c d
tar -xvzf file.tar.gz
另外,假如tar命令压缩绝对路径文件时,需要特别注意,不能如下面这样:
tar -czf /tmp/file.tar.gz /smbshare/a /smbshare/b /smbshare/c
上面这条命令本意是,在压缩时,加上全路径,并把压缩文件放在/tmp目录下(至于为什么不先进入/smbshare目录, 因为我是在某次工作需求中,需要通过程序执行shell命令进行压缩。因此需要使用绝对路径!)
上述这个命令执行后,压缩文件里,也会把smbshar目录前缀压缩进去。
正确的命令应该如下,使用 -C 选项改变tar命令的临时工作路径:
tar -czf /tmp/file.tar.gz -C /smbshare a b c d
tar -czf /opt/cecgw/csmp/static/cloudwatch/filecheck/20170908-164114.tar.gz -C /opt/cecgw/csmp/static/cloudwatch/filecheck call_stack.log test.py test_1.py
4.4.25. crontab¶
准确来说,这并不是一个命令,而是Linux系统的一个定时服务!
通过编辑/etc/crontab文件,添加如下格式行,然后 service cron restart 重启cron服务,
定时任务就可以生效了。
minute hour day month week user cmd
每一列分别表示:分、小时、天、月、星期、用户、定时任务。
来看一个简单的需求。同事曾经编写的一个服务,总是会过一段时间异常退出,定位了很久无法解决。 最后要求我能不能用某种方式,定时判断服务是否关闭,如果关闭则重启。
这里以ssh服务类比为例,来满足这个需求。当然,最正确的方式,肯定是直接debug!
首先简单写一个脚本,判断ssh服务是否在运行,否则重启服务!
#! /usr/bin/env bash
num=`netstat -pltna | grep -P :22 | grep ssh | wc -l`
# 利用ps -ef | grep sshd 命令应该也可以。
#echo "num is, ", $num
if [[ $num -ge 1 ]]; then
:
#echo "IN IF: num is, ", $num
else
service ssh restart
fi
然后编辑/etc/crontab文件,追加上:
*/30 * * * * root bash /smbshare/ssh_restart.sh
然后重启cron服务就可以了。
4.4.27. 查看系统启动服务¶
initctl list | grep nova
4.5. Linux一行命令汇总¶
自己平时日常操作中写的一行命令汇总。由于自己对shell不是特别熟悉, 可能有些命令效率不是最高的。
# 列出目录下大小最大的前15个文件
ls -l | sed '1d'| awk '{print $5, $NF}'|sort -nr| head -15 | awk '{print $NF}' | xargs ls -hl